What is ginseng
Custom usage
Ginseng is a medicinal plant, from which the root is harvested after a long and
costly growing period of 4 to 6 years. Especially the dried ginseng root has been
appreciated and used for thousands of years in China to bring the body and mind
back into the natural balance. Ginsengs properties are both preventive and curative.
The typical qualities of ginseng are the so called adaptogenic properties:
a phytocomplex able to rebalance the function of the Central Nervous System together
with the bodily functions through improvement of the function of the tissue, organs
and systems.
In the Western world ginseng is mostly taken as a tablet, a capsule or elixir on a
daily bases for every days physical complaints. But also to become more resistant
against stressful situations, to get extra energy and to improve the natural immune-system
of the body.
Origin
The relatively small ginseng plant grows in the wild in an inclined area, in a dry sandy
soil and in dense forests from foliage trees. Ginseng originates from North East China,
North-Korea and Siberia, but also from the other side of the sphere, on the border of
Canada and the United States.
The Asian ginseng is called Panax CA Meyer (in popular language: Korean Ginseng) and the
North American: Panax Quinquefolium (in popular language: American ginseng).
Wildly harvested ginseng roots can become extremely old, but became very rare as well.
Because of this the value of wild ginseng roots is more worth than its weight in gold.
For this reason, over 50 years ago, one started to cultivate ginseng on farms. Due to
the cultivation of ginseng and protection as an endangered species the extinction of the
plant is prevented.
 |
Photo: a very rare old wild ginseng root is more worth than its weight in gold |
Yin en Yang
At a glance the ginseng plants and roots from Asia and North-America seems identical. From a TCM (=Traditional Chinese Medicine) point of view these two ginseng species are considered to be each others opposite.
Yin is cold or cooling energy. The American ginseng is therefore used for those with a surplus of Yang or a deficiency of Yin. |
 |
Yang is hot or warming energy. The Korean ginseng is therefore used for those with a surplus of Yin or a deficiency of Yang. |
In the Western world there is much less distinction used between both types of ginseng.
Especially the more stimulating Korean ginseng is prescribed, whereas the more calming and
regulating American ginseng would probably more appropriate in the current fast and stressful
society in which we live.
In general there can be said that both Korean and American ginseng contain the same active
components, but in both ginsengs they are present in relatively different proportions.
In majority this explains why both species can act the same but also as each others opposite.
Active components
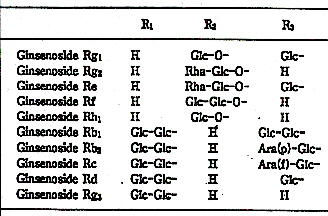
Typically for all the ginseng species of the genus Panax are the presence of the so-called ginsenosiden; the active components of ginseng. These ginsenosiden are tryterpene glycosides of the dammarane type:
 |
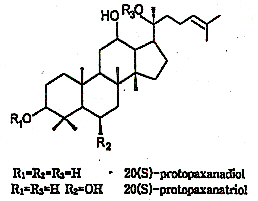 |
Each of the active components knows has its own specific actions. Ginseng contains each others
opposite active ginsenosides. For example ginsenoside Rg1 has stimulating actions while
ginsenoside Rb1 has tranquilising and calming actions.
It remains however the sum of the total ginsenosiden and other components in the ginseng root,
that cause the typical adaptogenic actions of ginseng. All of the components in the ginseng
root together also ensure that the actions never exceed the body's natural optimum.
Regulator
The active components of ginseng work jointly as a stimulator and regulator between nearly all organs & glands and the Central Nervous System (CNS). Because all these systems function better with ginseng, the whole body will function better, one will feel better and the whole body can perform (much) more without this being harmful to it.
Actions
The direct positive actions of ginseng on the organs, glands and CNS at the same time,
results in the body indirectly positive on a broad range of ailments and complaints:
1) Relatively simply to prove specific "medical" claims
- Cholesterol 4)14)
- blood sugars/diabetes 7)14)15)
- Bloodpressure 8)
- Lungs and bronchial tubes12)13)
- Migraine
- Resistance / immune system 2)12)13)15)
- Memory/concentration 3)5)6)9)11)15)
- Meno pause / hot flushes
- Sleeping behaviour 5)
- Energy/performance 5)6)15)
- Stress/tensions 1)
- Aphrodisiac
- Infirmities of old age 6)10)
- General well-being 5)6)10)
- Preventing ailments and complaints 5)9)10)12)13)
Scientific support
Most likely there is no other herb that has been researched scientifically so extensively then ginseng. The articles of the scientific prove for ginsengs actions you can find below. On your request we can send you copies from one or more of the following articles:
- Kim et al., 1969, Influence of Ginseng on the Stress Mechanism, Lloydia,Vol.33, no.1, 43-48.
- Scaglione F. et al, 1990, Immunomodulatory effects of two extracts of Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer, Drugs Exp.Clin.Res. XVI (10), 537-542.
- Sorensen Hendrik and Jesper Sonne, 1996, A double-masked study of the effects of Ginseng on Cognitive Functions, Current Therapeutic Research, Vol. 57, no.12, 959-968.
- Studer W.H., 1995, The use of American Ginseng (Panax Quinquefolium) in the amerlioration of symptoms of HDL Cholesterol deficiency syndrome, and the use of anecdotal evidence in identifying research opportunities in this disease, Proceedings of the Int. Ginseng Conf. - Vancouver 1994, 249-258
- Dörling E, 1980, Do Ginsenosides influence the Performance? Results of a doub1e blind study, Published in Notabene Medici, Vol. 10, no. 5, 241-246, (translated from German).
- Knipschild P., 1988, Ginseng Pep of Nep, Een overzicht van experimenten bij ouderen met stoornissen van de vitaliteit, Pharmaceutisch Weekblad, Jaargang 123, nr. 1, 123.
- Vuksan Vladimir et al., 2000, Similar Postprandial Glycemic reduction with escalation of dose and administration time of American Ginseng in Type 2 Diabetes, Original art. Publ. in Diabetes Care, Vol. 23, no. 9, 1221-1226.
- Vuksan Vladimir et al., 2000, American Ginseng improves Blood Pressure in Type 2 Diabetes, Summary.
- Attele Anoja S et al, 1999, Ginseng Pharmacology, Multiple constituents and multiple actions, Biochemical Pharmacology, Vol. 58, 1685-1695.
- Hong Soon Keun, Studies on the safety of Korean ginseng ingested as food substance, Korea Ginseng & Tobacco Research Institute, 199-213
- Larkin Marilynn, 1999, Surgery patients at risk for herb anaesthesia interactions, The Lancet, Vol. 354, 1362.
- Scaglione F. et aL, 1994, Immunomodulatory effects of Panax Ginseng C.A. Meyer (G115) on alveolar macrophages from patients suffering with Chronic Bronchitis, Int. J. Immunotherapy X(1),21-24.
- Scaglione F. et aL, 1996, Efficacy and safety of the standardized Ginseng Extract G115 for potentiating vaccination against common cold and/or influenza syndrome, Drugs Exptl. Clin. Res. XXII(2), 65-72.
- Yokozawa Takako et al.,1975, Effect of Ginseng extract on Lipid and Sugar metabolism. Metabolic correlation between liver and adipose tissue, Chem. Pharm. Bull., Vol.23 (12), 3095-3100.
- Vogler B.K. et al, 1999, The efficacy of ginseng. A systematic review of randomised clinical trials, Clin. Pharmacol., no. 55, 567-575.
